Short Question Solution
a. Enlist various objectives of Software Engineering.
Ans:
Objectives of Software Engineering
- Correctness – Ensure the software meets user requirements and functions as intended.
- Efficiency – Optimize resource usage like CPU time and memory.
- Maintainability – Make it easy to update, modify, and fix bugs.
- Scalability – Support future growth and additional features.
- Security – Protect against unauthorized access and threats.
- Reliability – Ensure software functions correctly under different conditions.
b.
Explain any
three uses of component diagram.
Ans:
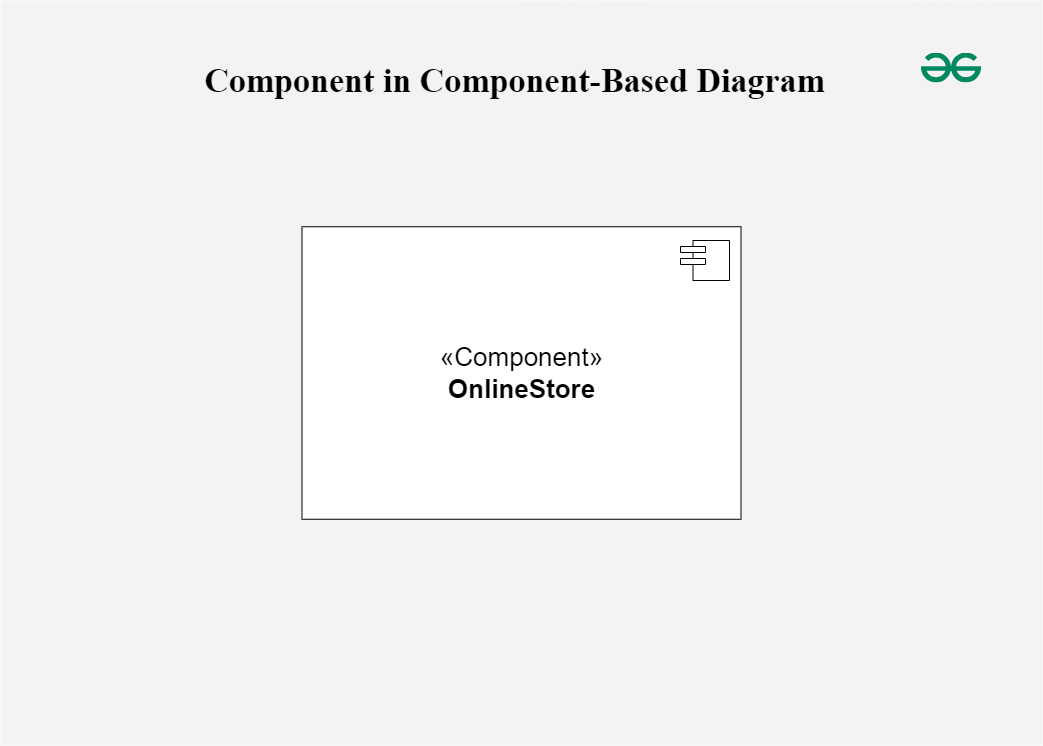
Uses of Component Diagram
- System Architecture Representation – Helps visualize the structure and dependencies between software components.
- Reusability – Identifies reusable software components to reduce development time.
- Dependency Management – Shows how different parts of the system interact, helping in understanding system dependencies.
Example: In an e-commerce application, a component diagram can show components like "User Authentication," "Product Catalog," and "Payment Gateway."
c.
Draw a neat
labelled diagram of prototype diagram.
Ans:
Prototype Model Diagram
A prototype model visually represents how the software will function before actual development.
Neatly labeled diagram (You can draw this based on the below description):
- User interacts with Prototype
- Prototype is tested and reviewed
- Feedback is given to the Development Team
- Necessary modifications are made
- Final system is developed
d.
Differentiate
Function point and Lines of Code.
Ans:
e.
Design a
test case table for login page with minimum four test cases.
Ans:
f.
Write
short note on six sigma approach.
Ans:
Six Sigma Approach:
- A data-driven methodology aimed at process improvement and variation reduction.
- It utilizes statistical tools and techniques to attain high levels of quality.
- The goal is to achieve near perfection, with a target of no more than 3.4 defects per million opportunities.
g.
Explain
Cohesion in Software.
Ans:
Cohesion refers to how closely related the tasks within a software module are. High cohesion means a module performs a single, well-defined function, improving maintainability and reusability.
Types of Cohesion:
- Functional Cohesion – Module performs a single function (Best).
- Sequential Cohesion – Output of one function is input to another.
- Logical Cohesion – Similar functions grouped together.
Example: A "Login Module" that only handles authentication (username & password) has high cohesion, whereas a module that also manages profile updates has low cohesion.
h.
What is
software reliability?
Ans:
Software reliability is the probability that software will perform without failure under specified conditions for a certain period. It is a key quality factor in software engineering.
Factors affecting reliability:
- Error Rate – Fewer bugs increase reliability.
- System Load – Performance under heavy usage.
- Fault Tolerance – Ability to recover from failures.
Example: A banking application must be highly reliable to process transactions without errors, ensuring customer trust.
i.
State
characteristics of software metrics.
Ans:
Software metrics are used to measure and analyze software quality, performance, and efficiency.
Characteristics:
- Measurable – Provides quantifiable results.
- Consistent – Produces the same result under similar conditions.
- Objective – Based on data, not opinions.
- Comparable – Helps in evaluating different projects.
Example: Defect Density (number of bugs per 1000 lines of code) is a common software metric.
k.
State
advantages and disadvantages of Waterfall model.
Ans:
Advantages:
- Simple & easy to manage – Each phase is clearly defined.
- Well-documented process – Helps in future maintenance.
- Best for small projects – Works well with clear requirements.
Disadvantages:
- Not flexible – Difficult to make changes once development starts.
- Late testing – Errors found late increase cost and time.
- Not suitable for large projects – Complex systems require iterative models.
Example: Used in small-scale projects like static websites but not suitable for large applications like social media platforms.
l.
Explain
Coupling in Software.
Ans:
Coupling refers to the degree of dependency between software modules. Lower coupling is better for maintainability and scalability.
Types of Coupling:
- Low Coupling (Good) – Modules work independently, reducing complexity.
- High Coupling (Bad) – Modules are tightly linked, making updates difficult.
Example: A "Payment Module" in an e-commerce site should be independent of the "User Profile Module", ensuring changes in one don’t affect the other.
m.
Mention
advantages of Extreme programming.
Ans:
Extreme Programming (XP) is an agile software development method that focuses on flexibility and customer satisfaction.
Advantages:
- Continuous Testing – Reduces bugs and improves software quality.
- Customer Collaboration – Frequent feedback ensures better alignment with user needs.
- Pair Programming – Two developers work together, improving code quality.
- Fast Development – Frequent releases allow early issue detection.
Example: XP is used in startups and rapid software development where quick updates are required.
n.
Explain the
function of Modules in Software.
Ans:
Modules in software help break down a program into smaller, manageable parts.
Functions of Modules:
- Encapsulation – Groups related functions together, improving organization.
- Reusability – Modules can be reused in different applications.
- Scalability – Allows easy addition of new features.
Example: A "User Management Module" in a web application handles login, registration, and profile updates separately from other modules like payments.
o.
Enlist the
importance of Software testing.
Ans:
Importance of Software Testing (3 Marks)
Software testing ensures that a system meets requirements and functions correctly.
Importance of Testing:
- Bug Detection – Identifies and fixes software errors before release.
- Security Assurance – Protects against cyber threats and data leaks.
- Performance Optimization – Ensures smooth and efficient software operation.
- User Satisfaction – Ensures that software meets customer expectations.
Example: A mobile banking app must be tested for security and transaction accuracy before deployment.



Comments
Post a Comment